What is an order book in trading?
If you’ve ever traded stocks, cryptocurrencies, forex, or any financial asset, you’ve likely come across the term “order book”. But what exactly is it?
An order book is a real-time, digital record of all the buy and sell orders for a specific asset on an exchange. It shows:
- Who wants to buy
- Who wants to sell
- The prices they’re willing to accept
Think of it like a marketplace notice board, filled with offers and asks, helping traders determine the current market price of an asset.
How does an order book work?
It organizes two main types of orders:
Bids
- These are buy orders, where traders specify how much they’re willing to pay for an asset.
Asks (Offers)
- These are sell orders, where traders set the price at which they’re willing to sell.
Whenever a seller’s ask price matches a buyer’s bid price, a trade takes place.
Example:
- Seller wants to sell Bitcoin for $60,000.
- Buyer wants to buy Bitcoin for $60,000.
- Result: A trade is executed at $60,000.
This constant matching of bids and asks is what causes prices in the market to rise and fall.
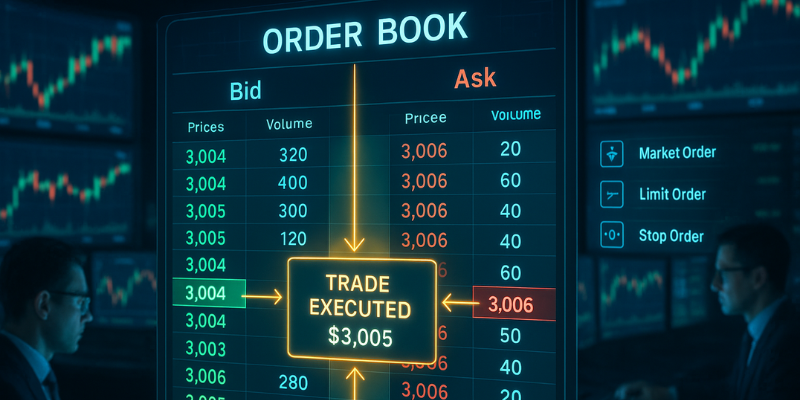
Key components of an order book
Understanding the structure of an order book is essential for successful trading. Let’s look at its main components:
- Price levels – These indicate the different prices at which traders want to buy or sell. Each price level can have multiple orders waiting to be filled.
- Order size (Volume) – This shows how much of the asset traders want to buy or sell at each price level.
Example: Several traders might want to buy a total of 10 Bitcoin at $59,900. - Bid and ask sides
Bid Side: Displays buy orders, listed from highest to lowest price.
Ask Side: Displays sell orders, listed from lowest to highest price. - Spread – The spread is the difference between the highest bid and the lowest ask.
A narrow spread suggests high liquidity and low volatility.
A wide spread signals low liquidity or market uncertainty.
The order book in action: A simple example
Let’s say:
- Highest bid for Ethereum = $3,000
- Lowest ask = $3,005
The spread here is $5.
If someone places a market buy order, it purchases Ethereum at $3,005—the lowest available ask. Once that order fills, the next lowest ask becomes the new asking price.
This dynamic matching is what makes prices fluctuate during trading.
Why the order book matters for traders
Understanding it is crucial because it:
- Reveals Market Sentiment: A surge in buy orders shows strong demand, while an influx of sell orders indicates selling pressure.
- Identifies Support and Resistance: Large clusters of buy or sell orders can create significant price barriers in the market.
- Helps Manage Slippage: Traders can see available liquidity and avoid placing orders that could cause drastic price moves.
How different order types affect the order book
Various types of trading orders interact with the order book differently:
Market orders
- Execute immediately at the best price available.
- Consume existing orders from the book.
Limit orders
- Sit in the order book until the market reaches the specified price.
Stop orders
- Activate only when the market hits a particular price, triggering either a market or limit order.
Understanding how your chosen order type affects the order book is key to managing trading costs and avoiding unexpected price changes.
Conclusion:
The order book is the heartbeat of financial markets. It reflects supply and demand, captures market sentiment, and provides valuable insights for making smarter trading decisions. Whether you’re trading stocks, cryptocurrencies, or forex, knowing how it works can give you a significant edge. Ready to learn more? Check out our other guides on trading strategies and market analysis to level up your skills!

