When diving into the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain, one of the first technical concepts you’ll encounter is Proof of Work (PoW). It’s the foundation that made Bitcoin and other early cryptocurrencies function without a central authority. But what does it actually do, and why is it so important?
In this article, we’ll break down the fundamentals of PoW, how it works, its advantages and drawbacks, and how it compares to newer consensus mechanisms.
What Is proof of work?
Proof of Work is a consensus algorithm used by blockchain networks to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain in a secure, decentralized manner. The “work” in Proof of Work is solving a math problem — a processor-intensive computational problem that requires a lot of processor power and time. The first computer (or miner) to solve the problem earns the right to add the next block on the blockchain and is rewarded in cryptocurrency (e.g., BTC).
It’s called “proof” because the miner must prove a measure of computational energy invested in building the block. It’s easy for others on the network to just double verify this proof, based on trust and consensus.
Why do blockchains require PoW?
Blockchains are decentralized networks. There’s no central server, no trusted third party, keeping a list of the transactions. Rather, all parties within the network must cooperate on the state of the blockchain.
And here’s the twist: How can a decentralized network agree on what valid transactions are, particularly when anyone can participate?
Enter PoW. It makes it:
- Hard to construct a block, which discourages spamming or fraud.
- Easy to validate the block, ensuring the network is in sync.
- Expensive to attack, where lots of computer power is required.
- On the whole, PoW prevents baddies from sneaking in and adding any transaction into the blockchain other than legitimate ones.
How does proof of work really work?
Let us observe how PoW works in a typical blockchain like Bitcoin:
- Unconfirmed transactions are stored in a memory pool (mempool).
- Miners select a set of transactions and place them in a candidate block.
- They begin to try to solve a cryptographic puzzle, that is, find a specific value (a nonce) such that, when appended to the data in the block, hashing produces something below a threshold value (the target difficulty).
- The try is attempting to try trillions of combinations—this is the “work.”.
- When a miner finds a valid solution, they broadcast the block on the network.
- All other nodes verify the solution and, if equalized, include the block within the blockchain.
- The successful miner is also rewarded with a block reward (new money + transaction fees).
- All of this takes place roughly every 10 minutes on the Bitcoin network.
Benefits of proof of work
Security: Altering previous information would result in re-doing the PoW for all subsequent blocks, which is impossible short of taking control of most of the world’s mining power.
Trustless validation: No need for a central authority—mere math proofs.
Proven track record: Bitcoin has been secure under PoW since 2009.
Criticism and limitations
PoW is secure, but it’s not perfect:
- Energy consumption: Mining is an enormous energy consumer. The Bitcoin network will be able to consume as much power as entire countries by some estimates.
- Hardware dependence: Mining is controlled by ASIC computers and massive mining farms, leading to centralization.
- Slower speeds: Because a block will take time to produce (e.g., 10 minutes for Bitcoin), PoW blockchains have lower transaction rates than newer protocols.
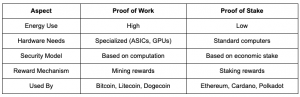
PoW vs. PoS (Proof of Stake)
As blockchain evolved, alternatives came in the form of Proof of Stake (PoS). Instead of relying on computer power, PoS selects validators depending on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are prepared to “stake” as collateral.
Ethereum, the second largest cryptocurrency, made the switch from PoW to PoS in 2022 on environmental and scalability bases.
Why PoW still matters
Despite all its flaws, Proof of Work is a pillar technology within the blockchain space. It was the first successful decentralized finance consensus algorithm and has endured for over a decade.
Bitcoin itself, the biggest and most secure blockchain, is still PoW-based, and many lay the success of it at its unparalleled security and predictability.
Final thoughts
Proof of Work is the initial trust engine of blockchain. It’s what makes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin secure, decentralizes them, and censorship-proof. Though newer designs like Proof of Stake are gaining traction on the basis of efficiency, PoW remains the heart of the crypto system.
Being attentive to how networks validate transactions and lock up data is central to automated trading and building. With Junglebot, we create software that is sensitive to the nuances of each blockchain network—i.e., whether a token is a PoW or PoS network. Users can then propel their trading logic to the extreme based on velocity, price, and network dynamics.

